Celiac Disease Endoscopy Findings
Celiac disease endoscopy findings. Upper endoscopy therefore takes on paramount importance in management of CD for several reasons including serendipitous discovery of endoscopic markers of CD. Practical importance for the diagnosis of celiac disease in children. Endoscopy of Celiac Disease - YouTube.
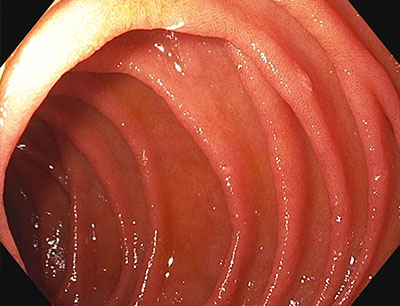
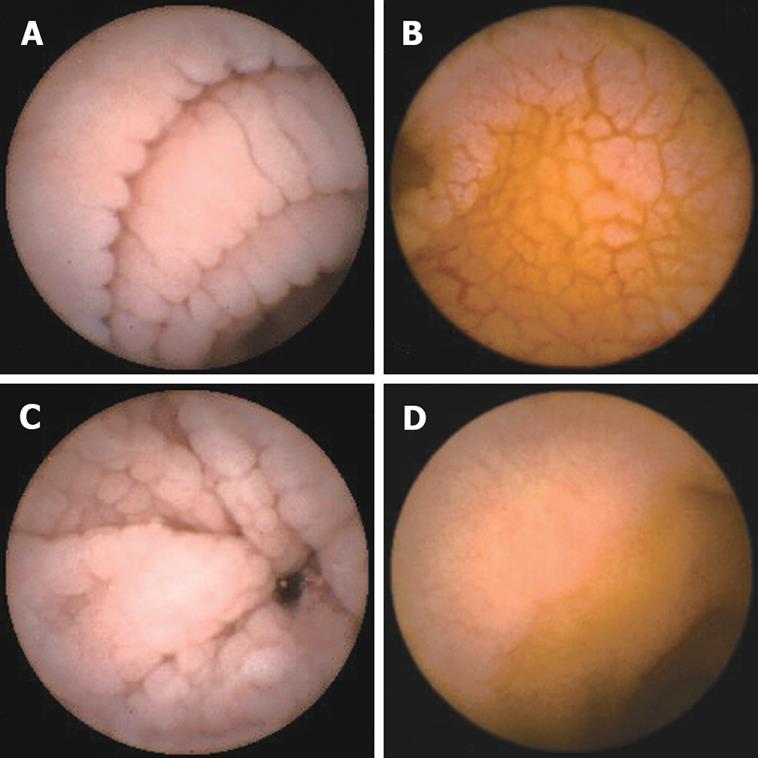
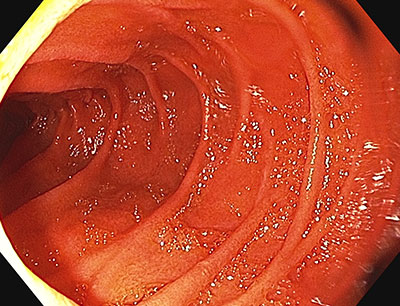
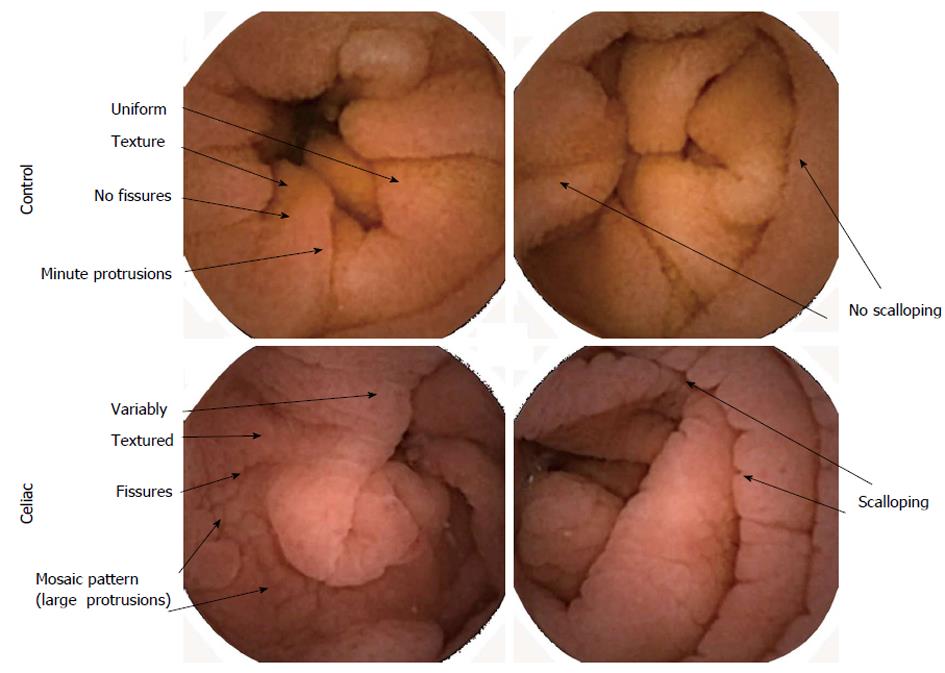
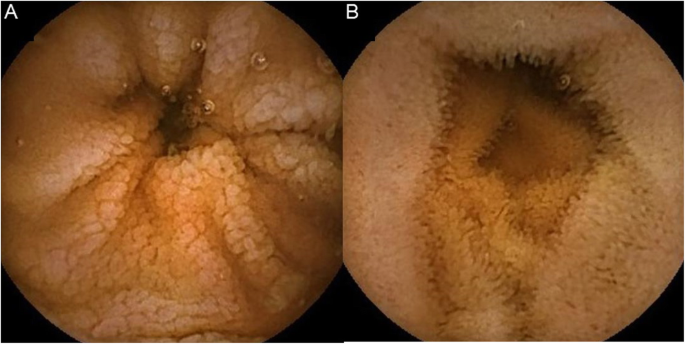
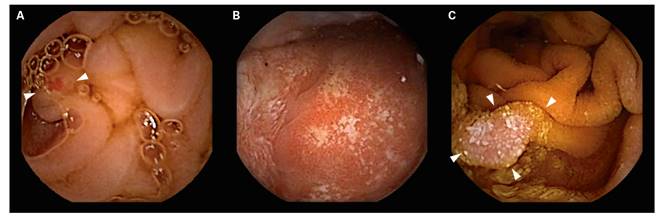
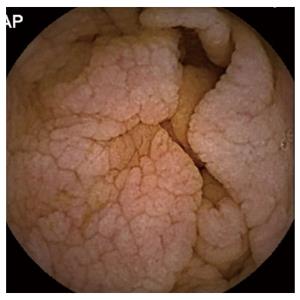
Scalloping mosaic pattern reduced fold height and nodularity are main endoscopic markers of celiac disease in children. The characteristic appearance of the surface of the small intestine in celiac disease includes superficial ulcerations that are commonly linear flattening of the folds notching or scalloping of the folds and a mosaic-like pattern. Evidence is presented that the endoscopic markers of celiac disease are specific although not sensitive for the disease.
This study shows for the first time that endoscopic recovery is faster than histological recovery in adults with celiac disease who go on a GFD. Endoscopy of Celiac Disease. Atrophy 68 fissuring 62 and mosaic pattern 19 extending to the ileum in 34.
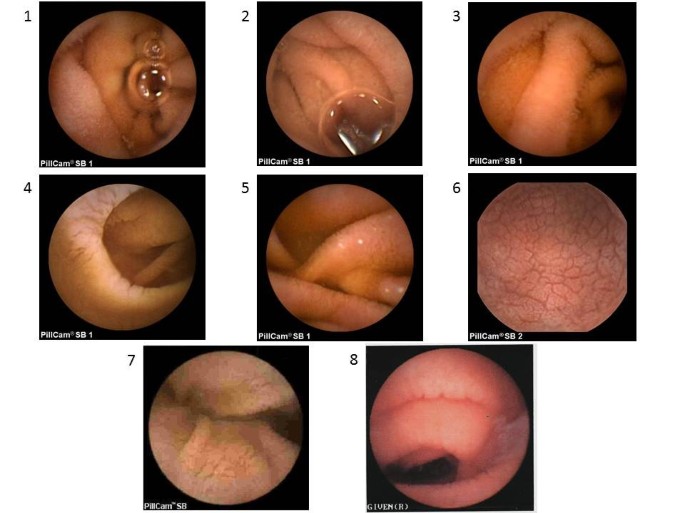
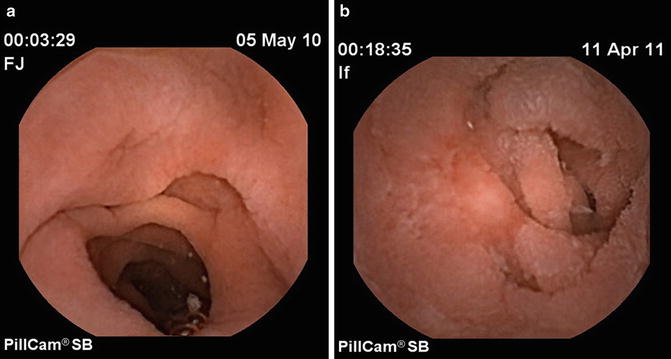
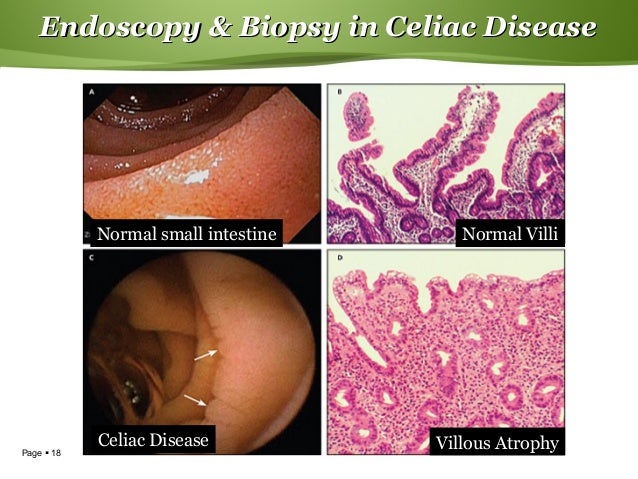
Villous atrophy the hallmark of celiac disease is patchy in the duodenum and various techniques may identify areas of villous atrophy. Video capsule endoscopy findings in celiac disease showing a c omplete mucosal recovery b s evere villous atrophy despite glutenfree diet c ulcerative jejunoileitis arrows in refractory sprue d i ntestinal stricture and suspicion of lymphoma. One subject with normal capsule endoscopy findings showed Marsh IIIc on duodenal histology.
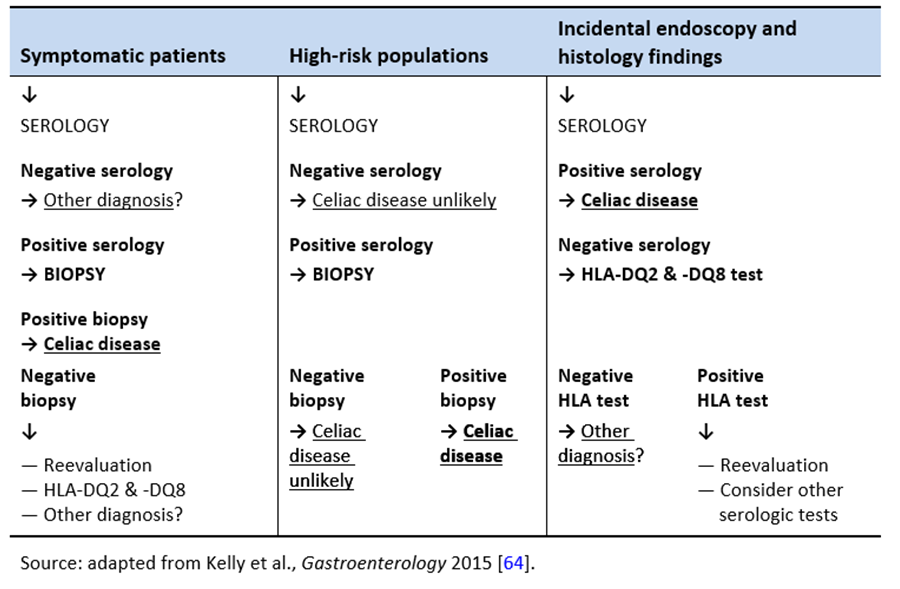
A 2-year prospective study. Although serology-based diagnosis of celiac disease CD in children recently has been legitimized 1 small bowel biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis of the condition 23. Endoscopy may show scalloping or flattening of duodenal folds fissuring over the folds and a mosaic pattern of mucosa of folds.
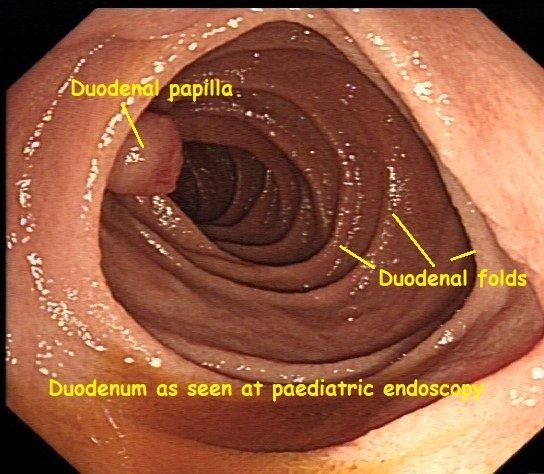
Celiac sprue that does not respond to gluten free diet of 6 - 12 months. 5 linhas A number of endoscopic findings have been described in adult patients with CD namely a mosaic. It is recommended that the doctor take at least 4-6 duodenal samples from the second part of duodenum and the duodenal bulb in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis.
Those who have the standard clinical symptoms of celiac disease such as sensitivity to gluten irritability abdominal pain or a positive blood test may undergo an endoscopy to confirm their diagnosis. Findings were consistent with celiac disease in 87.
Endoscopy of Celiac Disease.
Endoscopic markers of duodenal mucosa may be important in early diagnosis of celiac disease in children subjected to endoscopy for atypical presentations. A number of studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between the endoscopic duodenal findings and celiac disease. In the 14 subjects with duodenal histology that was consistent with celiac disease 13 had celiac disease changes seen at capsule endoscopy. Scalloping mosaic pattern reduced fold height and nodularity are main endoscopic markers of celiac disease in children. Although serology-based diagnosis of celiac disease CD in children recently has been legitimized 1 small bowel biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis of the condition 23. Endoscopy of Celiac Disease. A 2-year prospective study. Atrophy 68 fissuring 62 and mosaic pattern 19 extending to the ileum in 34. Villous atrophy the hallmark of celiac disease is patchy in the duodenum and various techniques may identify areas of villous atrophy.
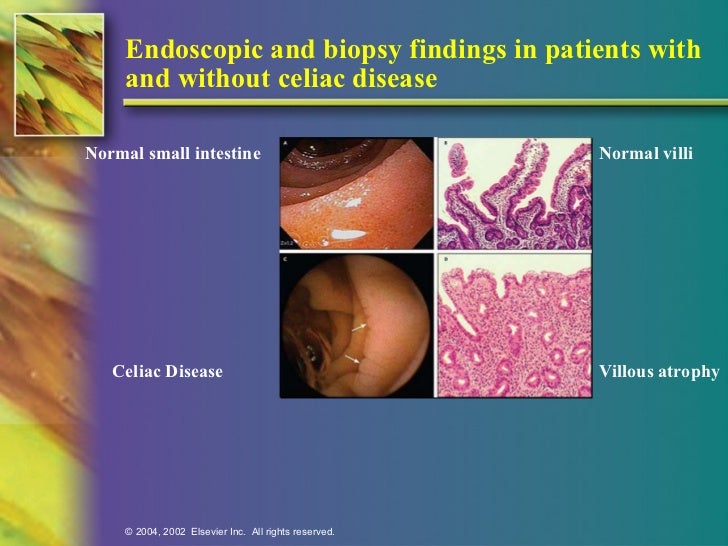
It is recommended that the doctor take at least 4-6 duodenal samples from the second part of duodenum and the duodenal bulb in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. Endoscopic markers of duodenal mucosa may be important in early diagnosis of celiac disease in children subjected to endoscopy for atypical presentations. Although serology-based diagnosis of celiac disease CD in children recently has been legitimized 1 small bowel biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis of the condition 23. During the procedure doctors take samples of tissue a biopsy from the small intestine to see if there is damage or flattening of villi. The characteristic appearance of the surface of the small intestine in celiac disease includes superficial ulcerations that are commonly linear flattening of the folds notching or scalloping of the folds and a mosaic-like pattern. Samples of the lining of the small intestine will be studied under a microscope to look for damage and inflammation due to celiac disease.





























Posting Komentar untuk "Celiac Disease Endoscopy Findings"