Paget Schroetter Syndrome Radiology
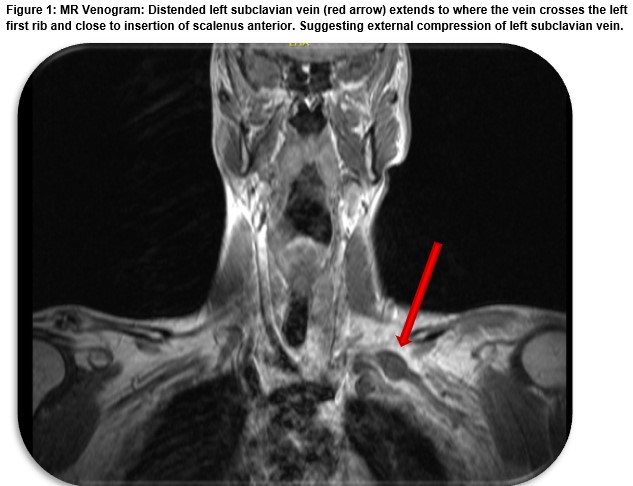
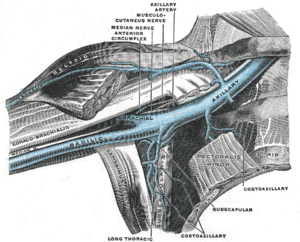
Paget schroetter syndrome radiology. Paget-Schrötter syndrome alternatively spelt Paget-Schroetter syndrome and also known as effort thrombosis refers to primary thrombosis of the axillary andor subclavian vein. Paget Schroetter Syndrome is a type of thoracic outlet syndrome. These were due to a combination of 1 an acquired hypercoagulability from minimal change disease and 2 dynamic anatomic narrowing of the subclavian vein which is known as Paget-Schroetter syndrome.
Thoracic outlet syndrome TOS is a rare clinical entity with many etiologies. It is neither positional nor secondary to indwelling catheters. Here we will focus on the pathophysiology anatomy clinical presentation treatments and outcomes of.
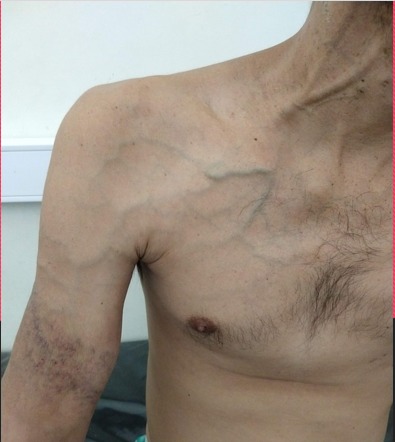
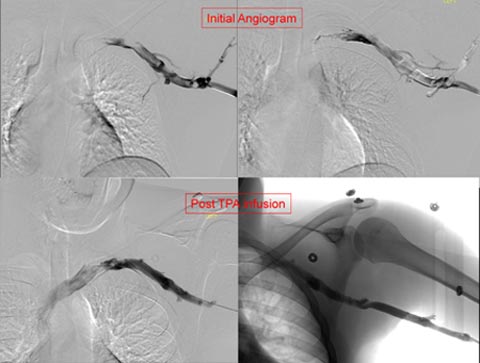
Paget Schroetter is deep vein thrombosis related to effort. Thrombolysis has been shown to be a safe and effective method of reestablishing venous patency in both primary and secondary axillosubclavian vein thrombosis. Sequelae of upper extremity deep vein thrombosis UEDVT are similar to those for lower extremity deep vein thrombosis LEDVT and incl.
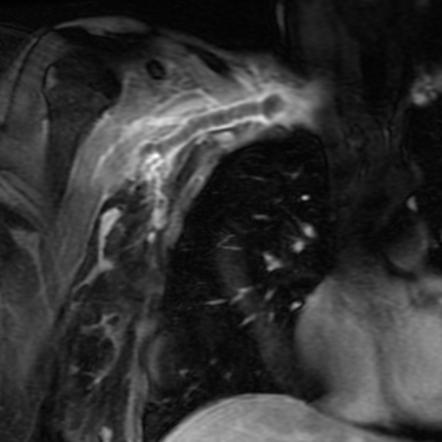
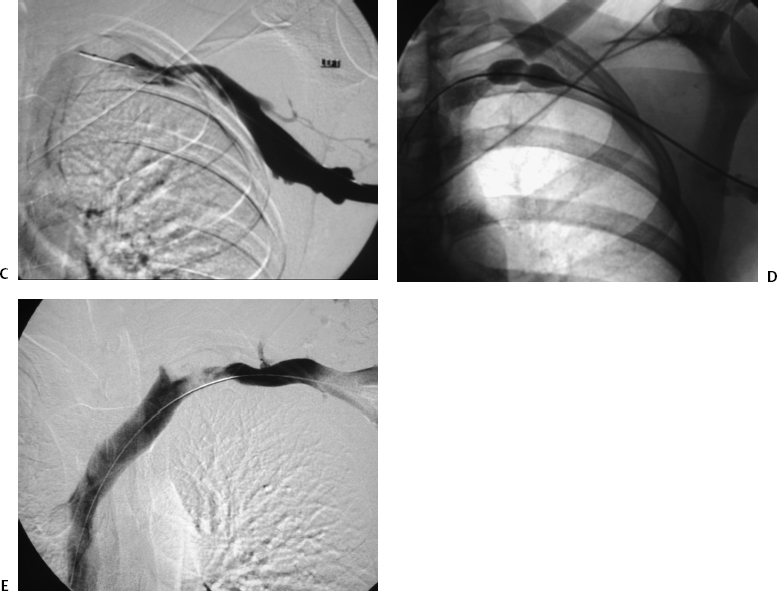
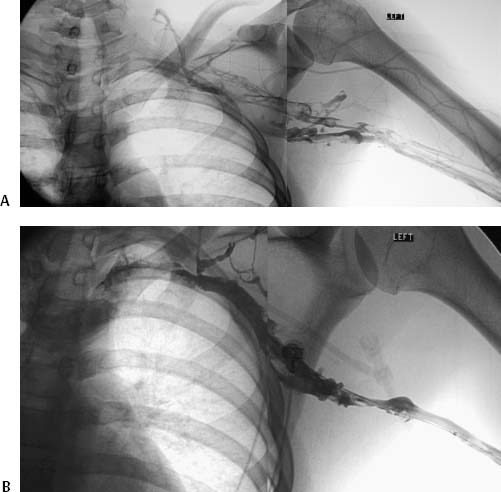
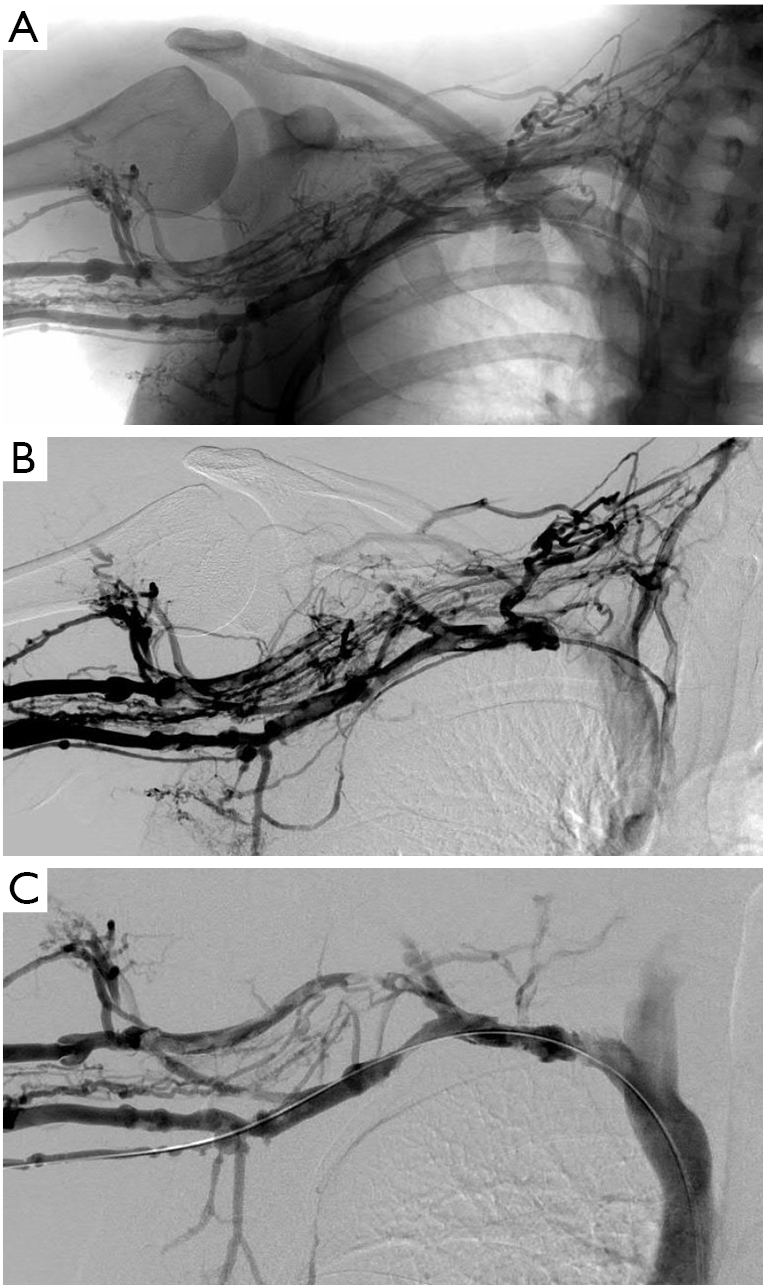
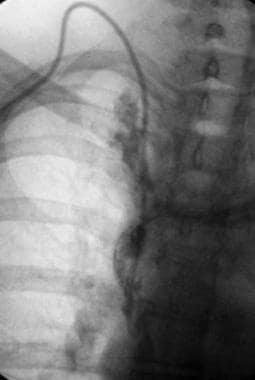
B Left-arm venogram after catheter-directed infusion of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for 4 hours shows partial thrombolysis. Paget-Schroetter syndrome is a rare disorder that may be difficult to diagnose and that typically affects young healthy active individuals. Paget-Schroetter syndrome PSS is a rare form of thoracic outlet syndrome caused by axillosubclavian vein thrombosis which typically presents in healthy young adults.
Most patients present with spontaneous axillosubclavian thrombosis also known as effort thrombosis or Paget-Schroetter syndrome although some can present with symptoms of intermittent venous compression in the absence of thrombosis McCleery syndrome 2 17 18. It can be thought of as a venous equivalent of thoracic outlet syndrome - ie venous thoracic outlet syndrome. Here we will focus on the pathophysiology anatomy clinical presentation treatments and outcomes of VTOS.
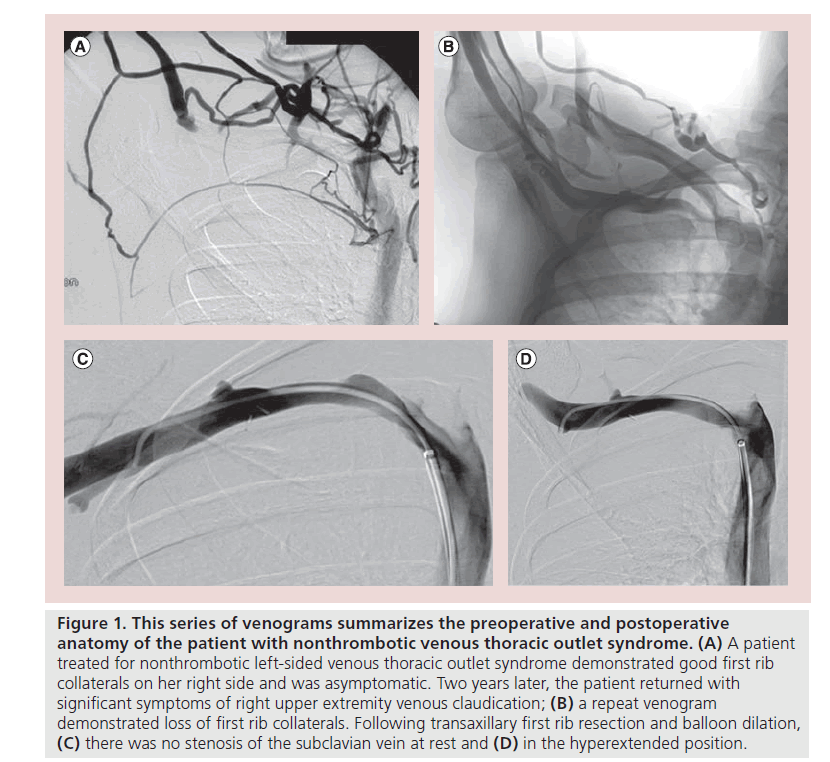
Paget-Schroetter syndrome PSS results from venous compression at the thoracic outlet leading to deep venous thrombosis. 1 2 3 PSS is a subset of thoracic outlet syndrome which also describes nerve arterial andor venous impingement at the thoracic outlet. Prompt therapy traditionally by means of catheter-directed thrombolysis CDT prior to definitive surgery can prevent the subsequent onset of postthrombotic syndrome PTS and considerable disability.
Paget-Schrötter syndrome alternatively spelled Paget-Schroetter syndrome and also known as effort thrombosis refers to primary thrombosis of the axillary andor subclavian vein. Treatment strategies including early and delayed surgical options are discussed to.
These were due to a combination of 1 an acquired hypercoagulability from minimal change disease and 2 dynamic anatomic narrowing of the subclavian vein which is known as Paget-Schroetter syndrome.
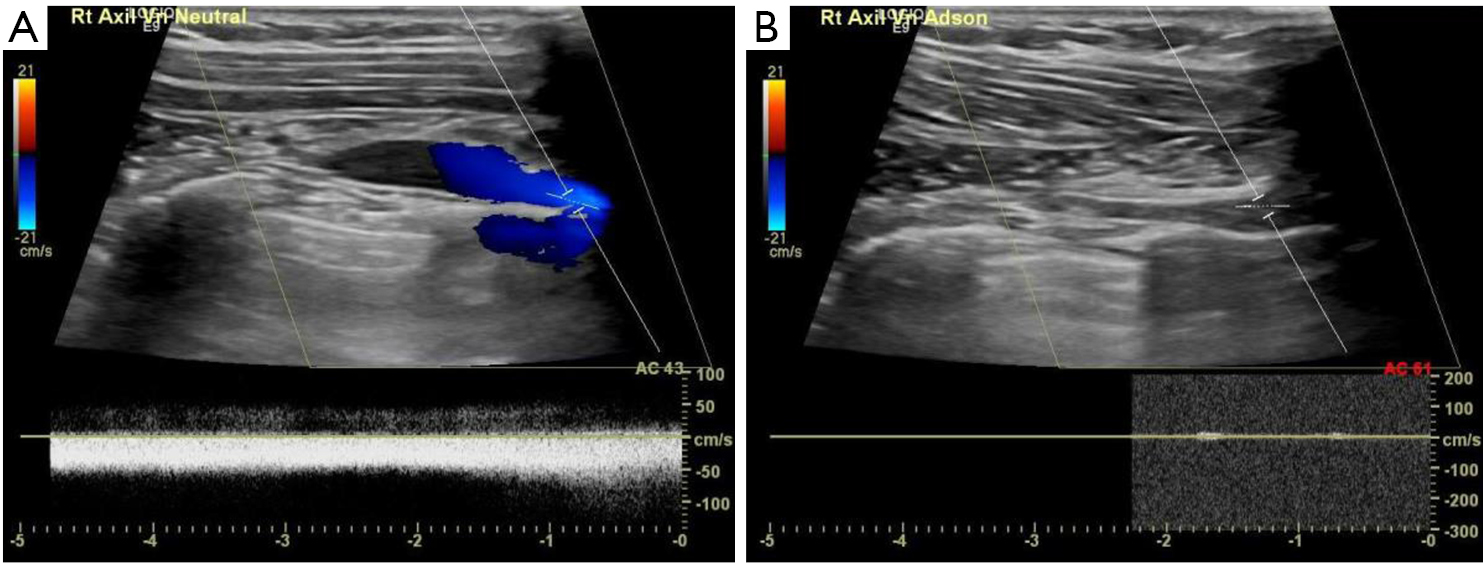
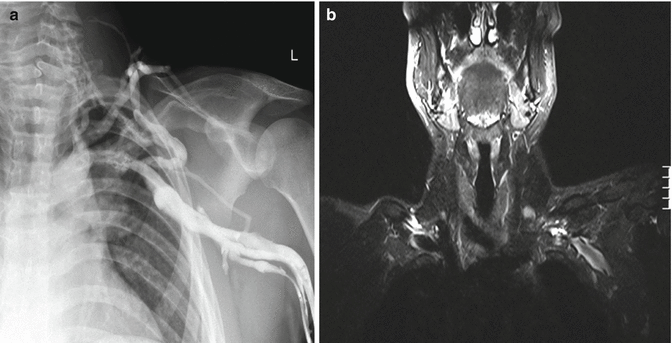
Venous thoracic outlet syndrome VTOS also called Paget-Schroetter syndrome PSS is a primary effort thrombosis. Paget Schroetter is deep vein thrombosis related to effort. Here we will focus on the pathophysiology anatomy clinical presentation treatments and outcomes of. Here we will focus on the pathophysiology anatomy clinical presentation treatments and outcomes of VTOS. PagetSchroëtter syndrome or primary thrombotic occlusion of the axillarysubclavian vein is diagnosed in a 42yearold man subsequently treated with thrombolysis and anticoagulation. Paget-Schroetter syndrome PSS results from venous compression at the thoracic outlet leading to deep venous thrombosis. It can be thought of as a venous equivalent of thoracic outlet syndrome - ie venous thoracic outlet syndrome. Paget-Schroetter syndrome PSS is a rare form of thoracic outlet syndrome caused by axillosubclavian vein thrombosis which typically presents in healthy young adults. Venous thoracic outlet syndrome VTOS also called Paget-Schroetter syndrome PSS is a primary effort thrombosis.
Thrombolysis has been shown to be a safe and effective method of reestablishing venous patency in both primary and secondary axillosubclavian vein thrombosis. A Left-arm venogram performed by contrast injection of a left-hand IV shows thrombosis of the brachial axillary and subclavian veins. Approximately 10 of all deep vein thromboses occur in the upper extremity and that number is increasing due to the use of peripherally inserted central catheters. 1 2 3 PSS is a subset of thoracic outlet syndrome which also describes nerve arterial andor venous impingement at the thoracic outlet. Treatment strategies including early and delayed surgical options are discussed to. Thrombolysis has been shown to be a safe and effective method of reestablishing venous patency in both primary and secondary axillosubclavian vein thrombosis. Paget-Schroetter syndrome is a rare disorder that may be difficult to diagnose and that typically affects young healthy active individuals.
































Posting Komentar untuk "Paget Schroetter Syndrome Radiology"