right sided homonymous hemianopsia
Homonymous hemianopsiaHomonymous hemianopsia as seen with left homonymous hemianopsia , or hemianopia, is a loss of visual field on the left or right side of the vertical line. It may affect an eye but usually affects both eyes. hemianopiaHomonymous hemianopsia (or homonymous hemianopia) is the hemonic loss of the visual field on the same side of both eyes. The homonymous hemianopsy occurs because the right half of the brain has visual paths for the left hemifield of both eyes, and the left half of the brain has visual paths for the right hemifield of both eyes. When one of these paths is damaged, the corresponding visual field is lost. Hemianopsiahomoníaco hemianopiaContentsSigns and symptoms[]Mobility can be difficult for people with homonym hemianopsy. "Patients often complain of colliding with obstacles on the side of the field loss, so their arms and legs sharpen." People with homonymous hemianopsy often experience discomfort in crowds. "A patient with this condition may not realize what he cannot see and often clashes with walls, travels on objects or enters people on the side where the field of view is missing." A related phenomenon is, the possible neglect of the right or the left. The patient is not aware of his existence. The right side of the face is not shaved, the composition is applied to one side of the face only and only half of a meal is eaten. This, however, is not necessarily due to a sensory anomaly, and therefore is different from hemianopsy. Causes[]Hungal hemianopsy may be congenital, but it is usually caused by brain injuries such as stroke, trauma, tumors, infection, or surgery. and (or malignant or benign) lesions of the , to cause a homonymous hemianopsy. The injury on the right side of the brain will affect the left visual fields of each eye. The further the brain injury, the more symmetrical (congruent) the homonymous hemianopsy. For example, a person who has a right injury will no longer see objects on his left side. Similarly, a person who has a hit to the right will have the same visual field defect, usually more congruent between the two eyes, and there may be. One on the right side of the brain (especially the parietal lobe), besides producing a homonymous hemianopsy, can also lead to hemispatial neglect syndrome. Hemianopsia homonima transoria does not necessarily mean trazo. For example, it may constitute migraine. The concomitant presence of a movement is suggestive of migraine, but it has also been seen in. (TC scan) or MRI can be used to investigate whether the stroke, tumor, structural injury or demitalization is the cause of the homonymous hemianopsy. Diagnosis[]Hemianopsia homonima secondary to occlusion – may result in memory impairment syndromes, opposite visual loss (Hynopsy homonym), and sometimes hemisensory deficits. The PCA supplies the occipital lobe and the medial part of the temporal lobe. Occipital cortex infarction usually causes macular spacing hemianopias due to the supply of dual blood both from the posterior cerebral artery and the middle cerebral artery. Inclusion of the calcarine artery that results in infarction of the upper part of the occipital lobe causes a lower defect of the peripheral visual field. The occlusion of the penetration branch of the posterior cerebral artery can result in infarction of the posterior capsule, causing hemisensory loss and (if it is low enough) a transient hemianopia may also occur. Management[]Prismos or "field extensions" that curve light have been prescribed for decades in patients with hemianopsy. Top Power Fresnel prisms ("adhesive") are commonly used because they are thin and light, and can be cut and placed in different positions in a spectacle lens. The spectacles of the peripheral prism extend the visual field of patients with visual defects of hemifield and have the potential to improve visual function and mobility. Prismatic shows incorporate superior power prisms, with variable shapes and designs. The prism of the Gottlieb button and the upper and lower horizontal bands are some patented examples of prism glasses. These high-power prisms "create" artificial peripheral vision in the non-blind field to avoid obstacles and motion detection. Some contrabalatory brain lesions have also shown improving visual deficits in a phenomenon known as the . Etymology[]Homonymous hemianopsy can be broken down as follows: The homonymous hemianopsy is also called the homonym hemianopia. ###################################################### #################################################################################################################################################################################################### Other Other binoculars subjective Other Inflammation Inflammation Inflammation Other Other Other binoculars subjective Other Other binoculars subjective Other Other binoculars subjective Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Other projects Languages

Homonymous hemianopia | definition of homonymous hemianopia by Medical dictionary

Homonymous hemianopsia - Wikipedia

Homonymous Hemianopsia - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Eye-Search - UCL's free therapy for visual search problems

Homonymous hemianopia • The Brain Recovery Project

Homonymous Hemianopsia - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
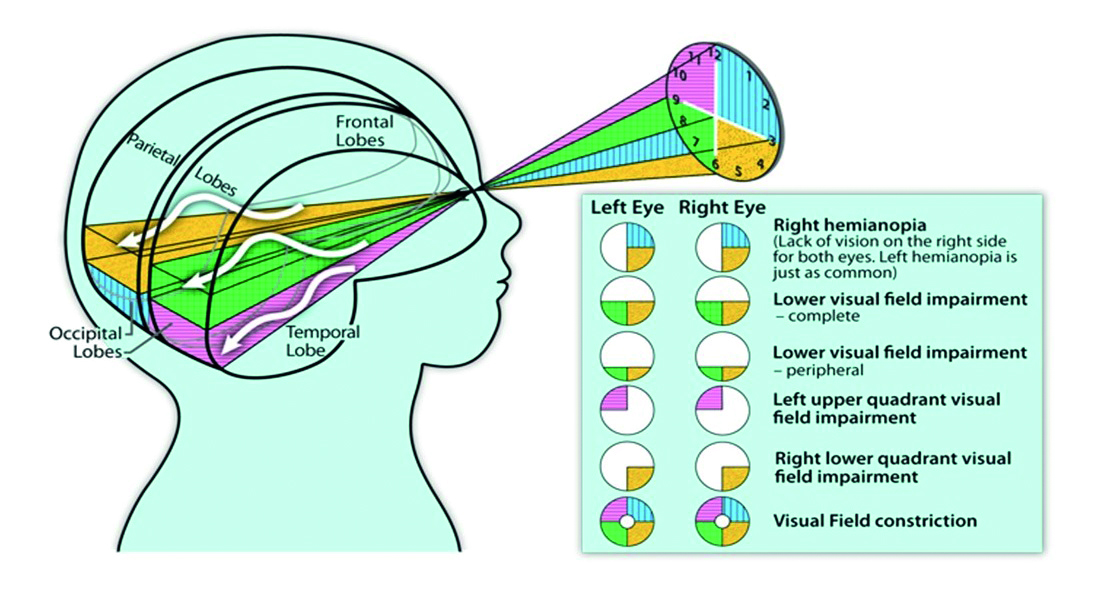
Optician
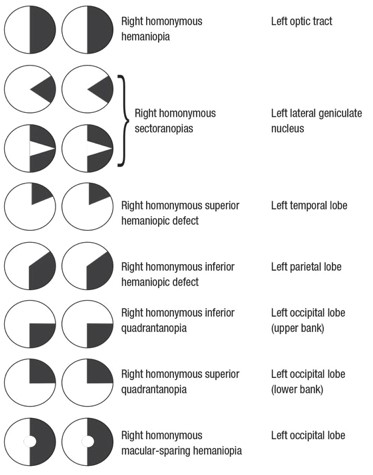
Not Your Typical Visual Field | Northwest Eye Surgeons
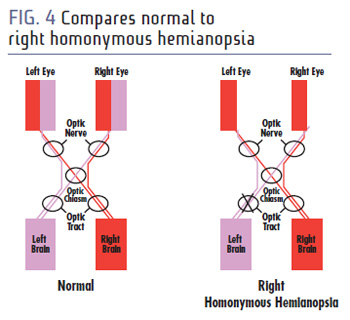
Lesson: WHY YOU DON'T WANT HOMONYMOUS HEMIANOPSIA AND WHAT YOU CAN DO FOR IT
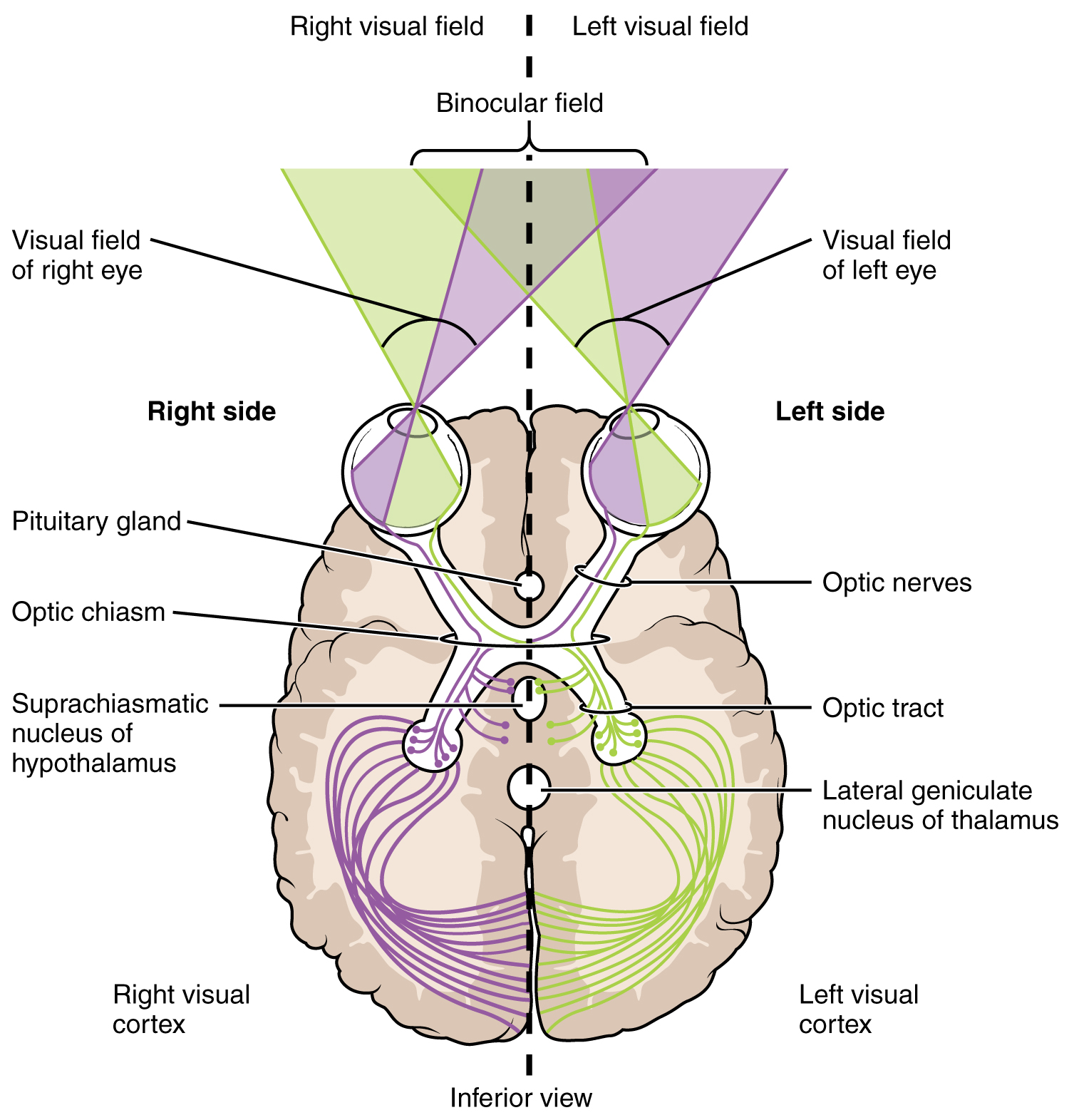
Homonymous hemianopia • The Brain Recovery Project
Your doctor thinks you have a homonymous hemianopia

CVI Scotland - Resources
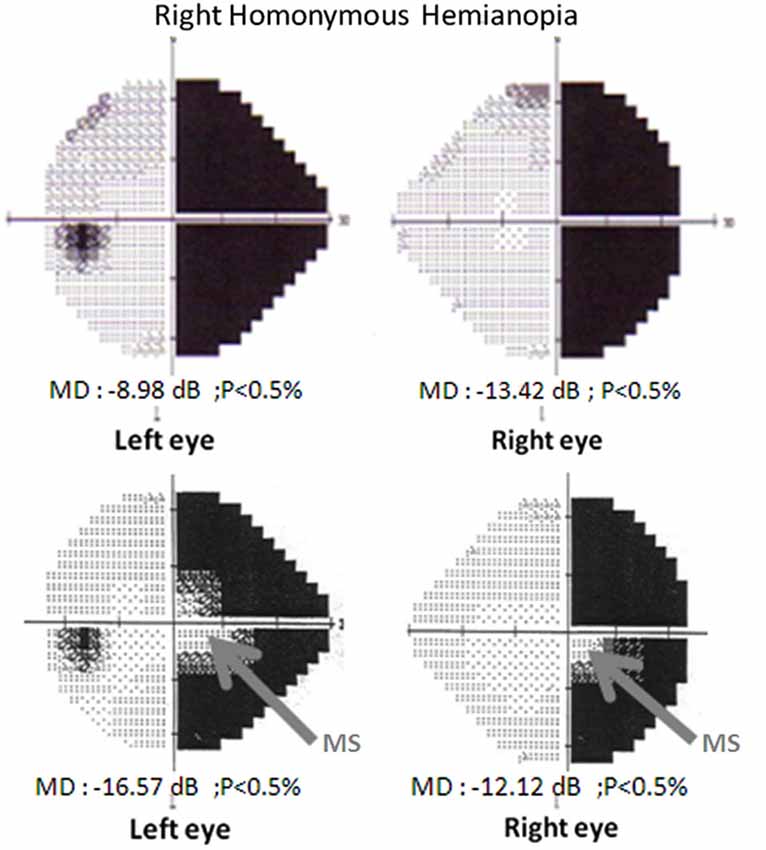
Frontiers | Rehabilitation of homonymous hemianopia: insight into blindsight | Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience

homonymous hemianopia | TBI Rehabilitation

Pin on Slp

Homonymous hemianopsia - Wikiwand

Hemianopia by Jenevieve Woon - issuu

Visual pathway lesions - Wikipedia
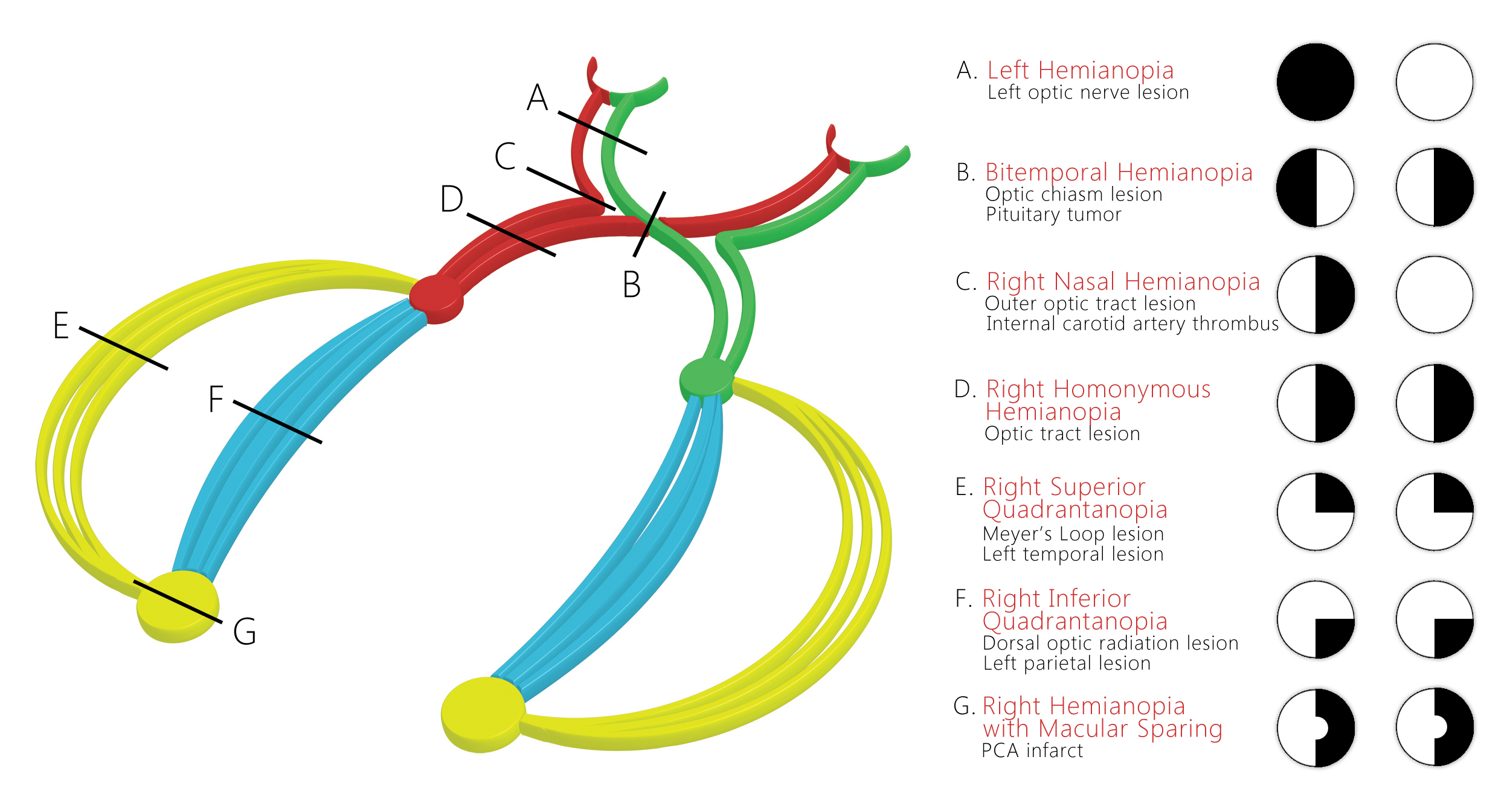
WBR0585 - wikidoc
Visual System (sensory System) Part 5

Managing a Case of Homonymous Hemianopia in a Young Adult
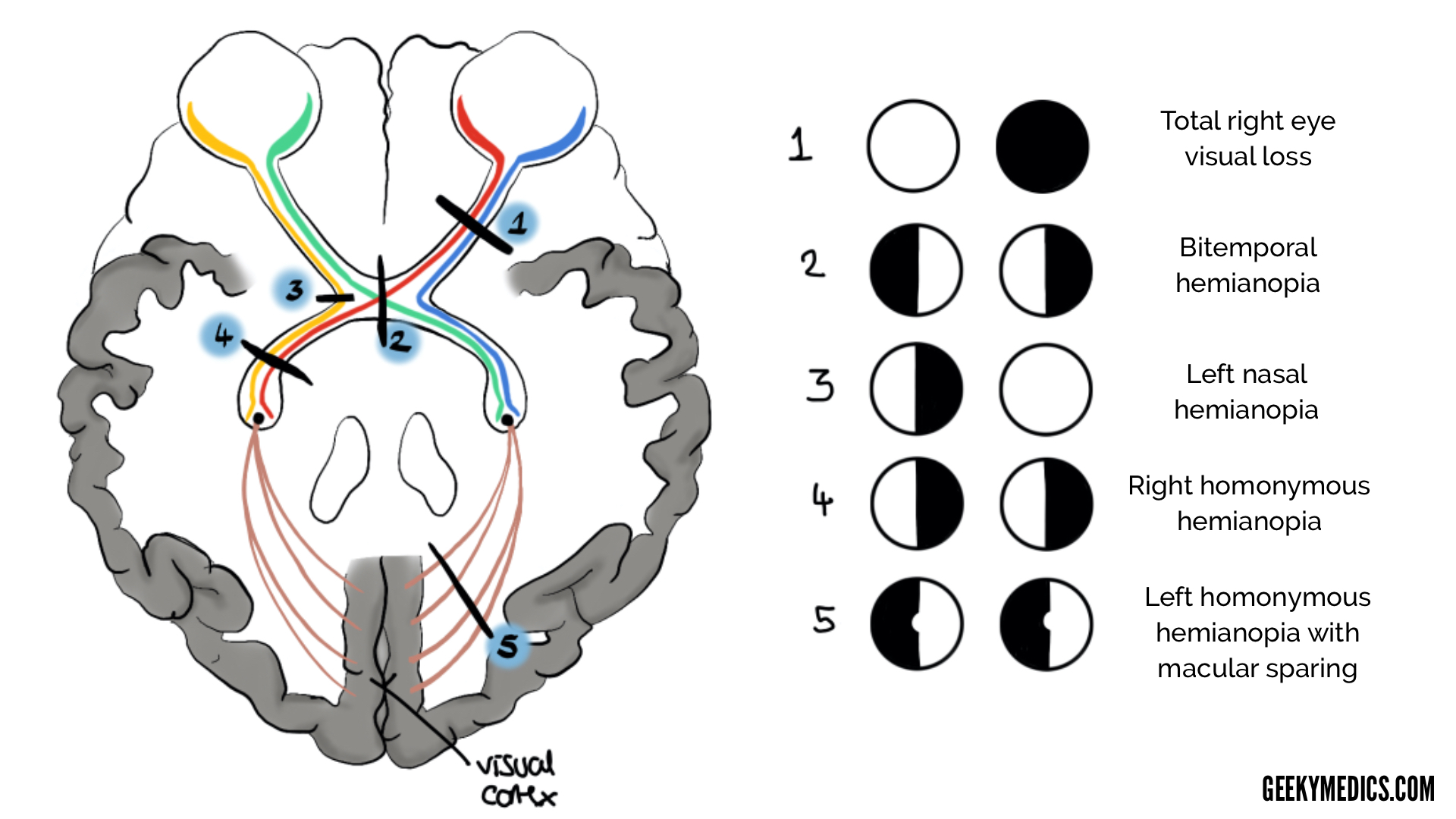
Visual Pathway and Visual Field Defects | Geeky Medics
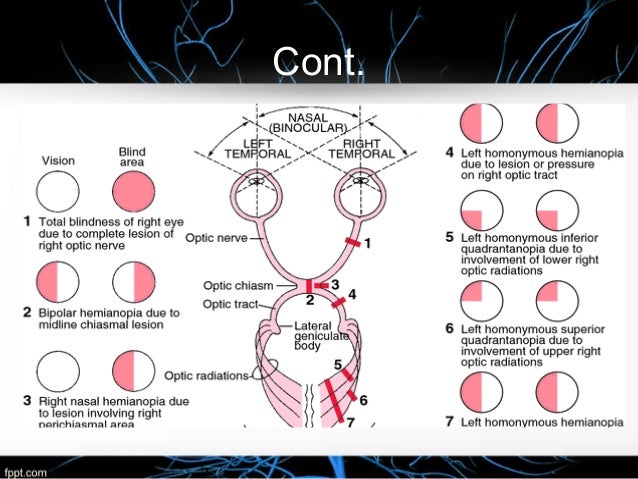
hemianopia

Decreased vision on the left side leads to hemianopia diagnosis

Visual fields obtained 2 days after admission, showing left homonymous... | Download Scientific Diagram

Homonymous Hemianopsia: Right Versus Left Hemispheric Injury | BrainLine

right homonymous hemianopsia - Google Search | Special needs kids, Vision impairment, Therapy
![Full text] Homonymous hemianopia: challenges and solutions | OPTH Full text] Homonymous hemianopia: challenges and solutions | OPTH](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s59000/59452/img/OPTH-59452-F01.jpg)
Full text] Homonymous hemianopia: challenges and solutions | OPTH

Examples of homonymous hemianopia with corresponding... | Download Scientific Diagram

Homonymous Hemianopsia - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Homonymous Hemianopsia, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment

Visual Field Defects

Homonymous hemianopsia

Hemianopsia - Rewellio
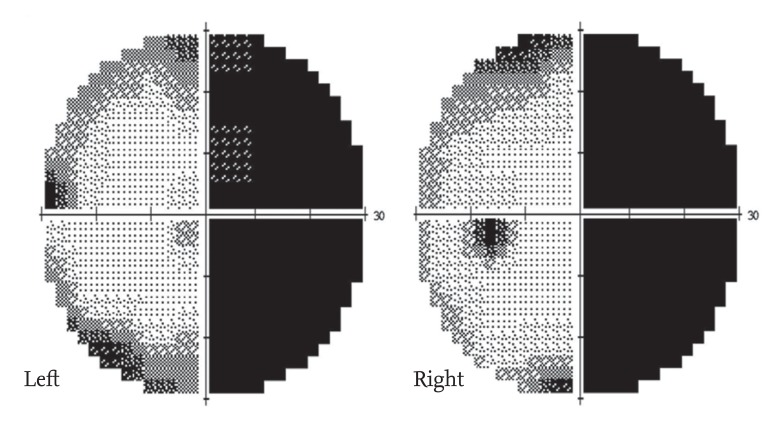
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine

Patient's left (A) and right (B) visual field showed a right-sided... | Download Scientific Diagram
![PDF] Case Study of Right-side Homonymous Hemianopia in a Stroke Patient Treated by Traditional Korean Medical Treatment | Semantic Scholar PDF] Case Study of Right-side Homonymous Hemianopia in a Stroke Patient Treated by Traditional Korean Medical Treatment | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/2e576ec1d0992da8cd0c3ce70df52ac90cae985b/2-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Case Study of Right-side Homonymous Hemianopia in a Stroke Patient Treated by Traditional Korean Medical Treatment | Semantic Scholar
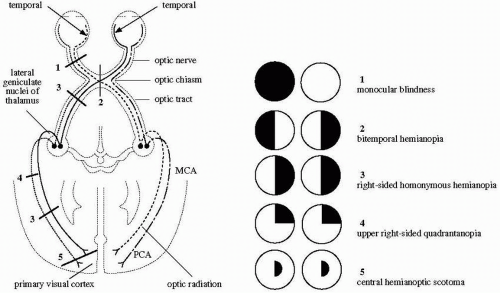
Eye: Orbit | Radiology Key
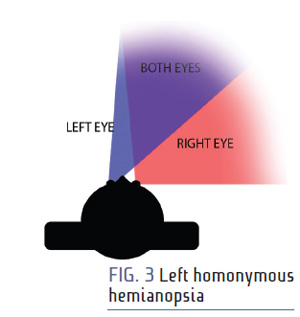
Lesson: WHY YOU DON'T WANT HOMONYMOUS HEMIANOPSIA AND WHAT YOU CAN DO FOR IT

Efficiency of Rarebit perimetry in the evaluation of homonymous hemianopia in stroke patients | British Journal of Ophthalmology
Posting Komentar untuk "right sided homonymous hemianopsia"